Definition of PLC
Programmable controller is a kind of digital operation electronic system, specially designed for application in industrial environment. It uses a programmable memory to store and execute logic operations, sequence control, timing, counting and arithmetic operations and other operating instructions in its internal storage.
And through digital and analog input and output, control various types of machinery or production processes. Programmable controllers and related peripheral equipment should be designed according to the principle of being easy to form a whole with the industrial control system and easy to expand its functions.

PLC classification
There are many types of PLC products, and their specifications and performance are also different. For PLC, it is usually classified roughly according to the difference of its structure, the difference of functions and the number of I/O points.
1. Classified by structure
According to the structure of PLC, PLC can be divided into two types: integral type and modular type.
(1) Integral PLC
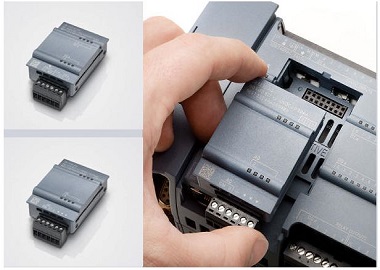
Integral PLC is to install the power supply, CPU, I/O interface and other components in a box, as shown in the figure. It has the characteristics of compact structure, small size and low price. Small-scale PLC generally adopts this kind of integral structure.
The integral PLC is composed of a basic unit (also called a host) with different I/O points and an expansion unit. The basic unit has a CPU, an I/O interface, an expansion port connected to the I/O expansion unit, and a programmer or EPROM write The interface connected to the input device, etc.; the expansion unit only has I/O and power supply, but no CPU.
The basic unit and the expansion unit are generally connected by a flat cable. Integral PLCs can generally be equipped with special function units, such as analog units, position control units, etc., to expand their functions.
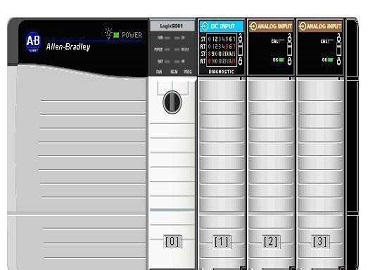
(2) Modular PLC
Modular PLC makes each component of PLC into several separate modules, such as CPU module, I/O module, power module (some included in CPU module) and various functional modules. Modular PLC is composed of a frame or base plate and various modules. The modules are installed on the socket of the frame or base plate, as shown in the figure.
This kind of modular PLC is characterized by flexible configuration, different scale systems can be selected according to needs, and it is easy to assemble, easy to expand and maintain. Large and medium-sized PLCs generally adopt a modular structure.
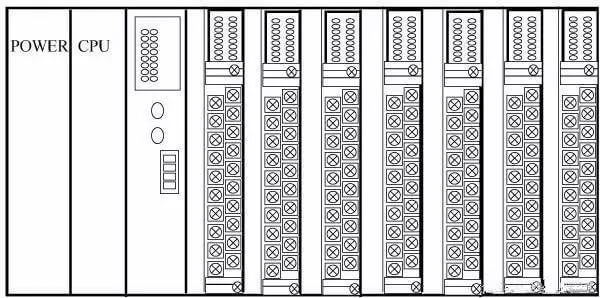
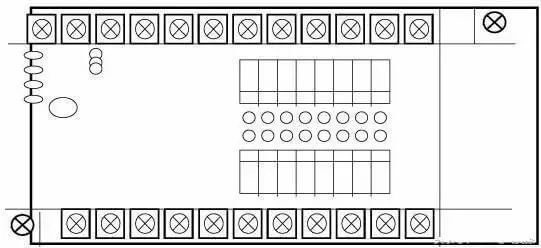
There are also some PLCs that combine the characteristics of the integral type and the modular type to form a so-called stacked PLC.
The CPU, power supply, I/O interface, etc. of the stacked PLC are also independent modules, but they are connected by cables, and each module can be stacked layer by layer. In this way, not only the system can be flexibly configured, but also can be made compact.

2. Classified by function
According to the different functions of PLC, PLC can be divided into three types: low-grade, middle-grade and high-grade.
(1) Low-grade PLC
Low-end PLC has basic functions such as logic operation, timing, counting, shifting, self-diagnosis, monitoring, etc. It can also have a small amount of analog input/output, arithmetic operation, data transmission and comparison, and communication. It is mainly used for logic control and sequence A single-machine control system for control or a small amount of analog control.
(2) Mid-range PLC
In addition to the functions of low-end PLCs, mid-range PLCs also have strong analog input/output, arithmetic operations, data transmission and comparison, number system conversion, remote I/O, subroutines, and communication networking functions; some can be added Interrupt control, PID control and other functions are suitable for complex control systems.
(3) High-end PLC
In addition to the functions of mid-range PLC, high-end PLC also adds signed arithmetic operations, matrix operations, bit logic operations, square root operations and other special function functions, tabulation and table transmission functions.
High-end PLC has a stronger communication networking function, can be used for large-scale process control or form a distributed network control system, and then realize factory automation.

3. Classified by I/O points
According to the number of I/O points of the PLC, the PLC can be divided into three categories: small, medium and large.
(1) Small PLC
The number of I/O points of a small PLC is less than 256, with a single CPU and 8-bit or 16-bit processor, and the user memory capacity is less than 4KB. For example: Mitsubishi FX0S series.
(2) Medium-sized PLC
The number of I/O points of the medium-sized PLC is 256-2048, with dual CPUs, and the user memory capacity is 2-8KB.
(3) Large PLC
The number of I/O points of a large-scale PLC is greater than 2048, with multiple CPUs and 16-bit or 32-bit processors, and the user memory capacity is 8-16KB.
In the world, PLC products can be divided into three major genres by region, one genre is American products, one genre is European products, and the other genre is Japanese products. The PLC technology of the United States and Europe is independently researched and developed under the condition of mutual isolation, so there are obvious differences between the PLC products of the United States and Europe.
The Japanese PLC technology was introduced by the United States and has a certain inheritance to American PLC products, but Japan’s main products are positioned on small PLCs. The United States and Europe are famous for large and medium PLCs, while Japan is famous for small PLCs.